


Μείνετε συντονισμένοι και παρακολουθήστε τις νεότερες εξελίξεις και νέα στην Μοριακή Ογκολογία.
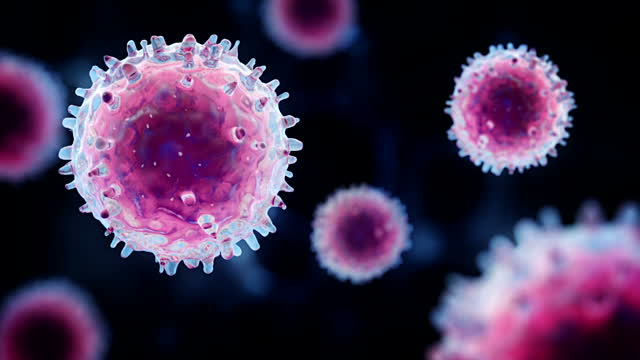
Immunotherapy, also called biologic therapy, is a type of cancer treatment that boosts the body’s natural defenses to fight cancer. It uses substances made by the body or in a laboratory to improve or restore immune system function.
An important part of the immune system is its ability to keep itself from attacking normal cells in the body. To do this, it uses “checkpoints” – molecules on immune cells that need to be turned on (or off) to start an immune response. Cancer cells sometimes use these checkpoints to avoid being attacked by the immune system. But newer drugs that target these checkpoints hold a lot of promise as cancer treatments.
Immunotherapy may work by:
Stopping or slowing the growth of cancer cells
Stopping cancer from spreading to other parts of the body
Helping the immune system work better at destroying cancer cells
There are several types of immunotherapy, including:
Monoclonal antibodies and tumor-agnostic therapies
Non-specific immunotherapies
Oncolytic virus therapy
T-cell therapy
Cancer vaccines
Monoclonal antibodies and tumor-agnostic therapies
When the body’s immune system detects something harmful, it produces antibodies. Antibodies are proteins that fight infection.
Monoclonal antibodies are a specific type of therapy made in a laboratory. They may be used in a variety of ways. For example, monoclonal antibodies can be used as a targeted therapy to block an abnormal protein in a cancer cell.
Monoclonal antibodies can also be used as an immunotherapy. For example, some monoclonal antibodies attach to specific proteins on cancer cells. This flags the cells so the immune system can find and destroy those cells.
Other types of antibodies work by releasing the brakes on the immune system so it can destroy cancer cells. PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 pathways are critical to the immune system’s ability to control cancer growth. These pathways are often called immune checkpoints. Many cancers use these pathways to escape the immune system. The immune system responds to the cancer by blocking these pathways with specific antibodies called immune checkpoint inhibitors. Once the immune system is able to find and respond to the cancer, it can stop or slow cancer growth.